Scaling Reads with Single Leader Replication in MySQL

One of the reasons for replication is to increase read throughput. This is done by scaling out the number of nodes that can serve read queries. In this blog post, we will setup one leader node (Leader Replica) to handle all write operations and three follower nodes (Follower Replica 1, 2 and 3) to process read requests. The leader node can also process read requests.
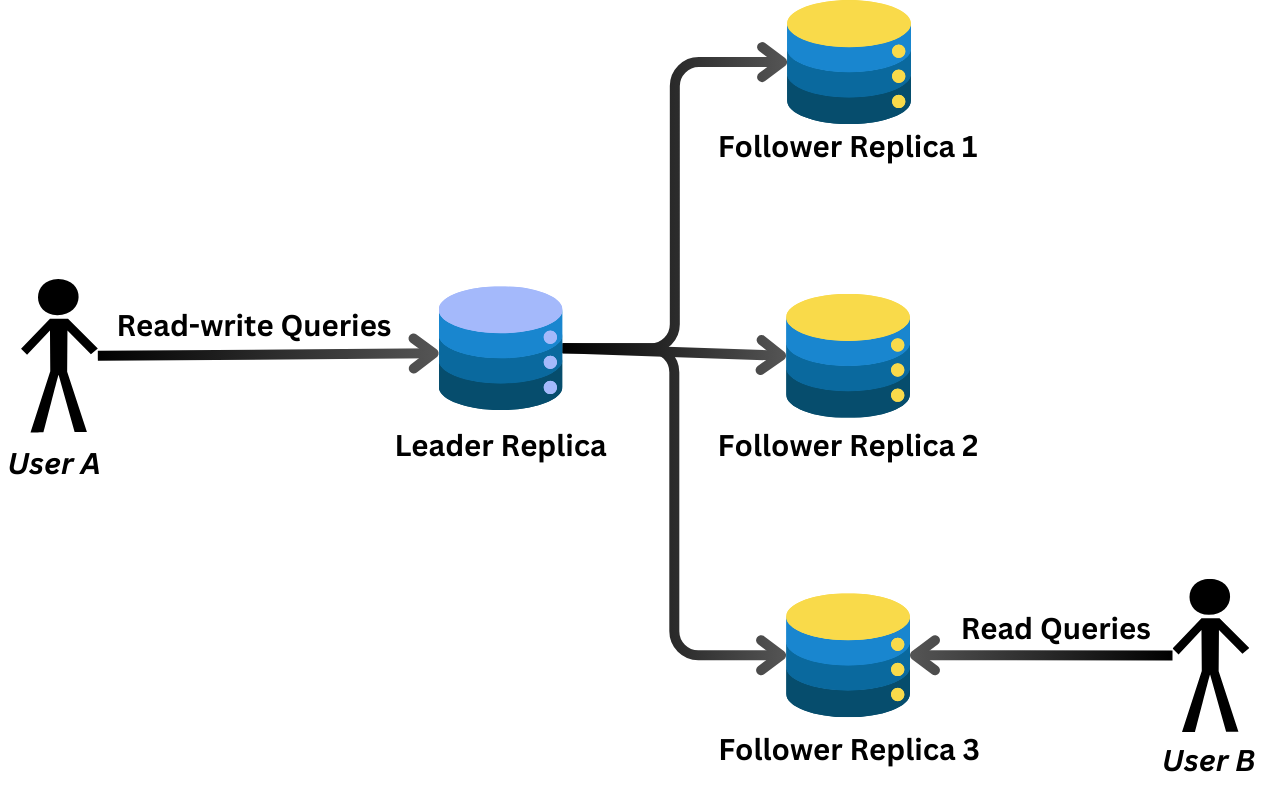
We will set this Single Leader Replication model using MySQL Docker containers.
1. Setup Docker Compose
version: '3.8'
services:
my-sql-write-read-replica:
image: mysql:8.0
container_name: my-sql-write-read-replica
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: Root1234!
MYSQL_DATABASE: ecommerce_db
MYSQL_USER: replica_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: Replica1234!
volumes:
- ./mysql-certs:/etc/mysql/certs
ports:
- "3306:3306"
command: >
--server-id=1
--log-bin=mysql-bin
--binlog-do-db=ecommerce_db
--require_secure_transport=ON
--ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/certs/ca-cert.pem
--ssl-cert=/etc/mysql/certs/server-cert.pem
--ssl-key=/etc/mysql/certs/server-key.pem
networks:
- mysql-net
restart: always
mysql-read-replica-1:
image: mysql:8.0
container_name: mysql-read-replica-1
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: Root1234!
MYSQL_DATABASE: ecommerce_db
MYSQL_USER: replica_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: Replica1234!
volumes:
- ./mysql-certs:/etc/mysql/certs
ports:
- "3307:3306"
command: >
--server-id=2
--log-bin=mysql-bin
--relay-log=slave-relay-bin
--read-only=ON
--require_secure_transport=ON
--ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/certs/ca-cert.pem
--ssl-cert=/etc/mysql/certs/client-cert.pem
--ssl-key=/etc/mysql/certs/client-key.pem
networks:
- mysql-net
restart: always
mysql-read-replica-2:
image: mysql:8.0
container_name: mysql-read-replica-2
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: Root1234!
MYSQL_DATABASE: ecommerce_db
MYSQL_USER: replica_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: Replica1234!
volumes:
- ./mysql-certs:/etc/mysql/certs
ports:
- "3308:3306"
command: >
--server-id=3
--log-bin=mysql-bin
--relay-log=slave-relay-bin
--read-only=ON
--require_secure_transport=ON
--ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/certs/ca-cert.pem
--ssl-cert=/etc/mysql/certs/client-cert.pem
--ssl-key=/etc/mysql/certs/client-key.pem
networks:
- mysql-net
restart: always
mysql-read-replica-3:
image: mysql:8.0
container_name: mysql-read-replica-3
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: Root1234!
MYSQL_DATABASE: ecommerce_db
MYSQL_USER: replica_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: Replica1234!
volumes:
- ./mysql-certs:/etc/mysql/certs
ports:
- "3309:3306"
command: >
--server-id=4
--log-bin=mysql-bin
--relay-log=slave-relay-bin
--read-only=ON
--require_secure_transport=ON
--ssl-ca=/etc/mysql/certs/ca-cert.pem
--ssl-cert=/etc/mysql/certs/client-cert.pem
--ssl-key=/etc/mysql/certs/client-key.pem
networks:
- mysql-net
restart: always
networks:
mysql-net:
driver: bridgeFew things to note about MySQL server replication options:
- --log-bin=mysql-bin - all database changes will be logged to a binary log file.
- --binlog-do-db=ecommerce_db - only log changes for a specific database (in this case ecommerce_db).
- --relay-log=slave-relay-bin - relay log stores changes sent from the leader node. The read replicas (followers) uses these logs to update its own database with those changes.
2. Spin up Containers
docker-compose up -d3. Configure the Leader
1. Access Leader Node
docker exec -it my-sql-write-read-replica mysql -u root -p2. Execute SQL
CREATE USER 'replica_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'Replica1234!';
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'replica_user'@'%';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;3. View Binary Log Status
SHOW MASTER STATUS;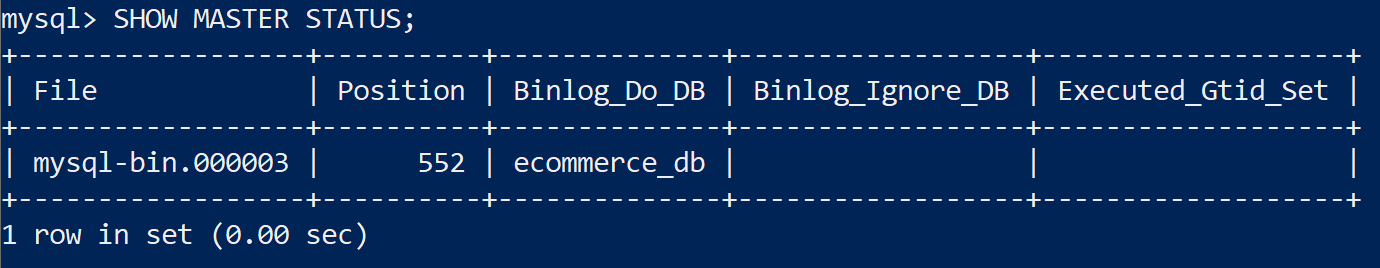
4. Configure Follower (Read Replica 1)
1. Connect to Read Replica 1
docker exec -it mysql-read-replica-1 mysql -u root -p2. Execute SQL
CHANGE MASTER TO
MASTER_HOST='my-sql-write-read-replica',
MASTER_USER='replica_user',
MASTER_PASSWORD='Replica1234!',
MASTER_SSL=1,
MASTER_SSL_CA='/etc/mysql/certs/ca-cert.pem',
MASTER_SSL_CERT='/etc/mysql/certs/client-cert.pem',
MASTER_SSL_KEY='/etc/mysql/certs/client-key.pem',
MASTER_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin.000003',
MASTER_LOG_POS= 552;
3. Start the Replica Node and Check Status
START SLAVE;
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G;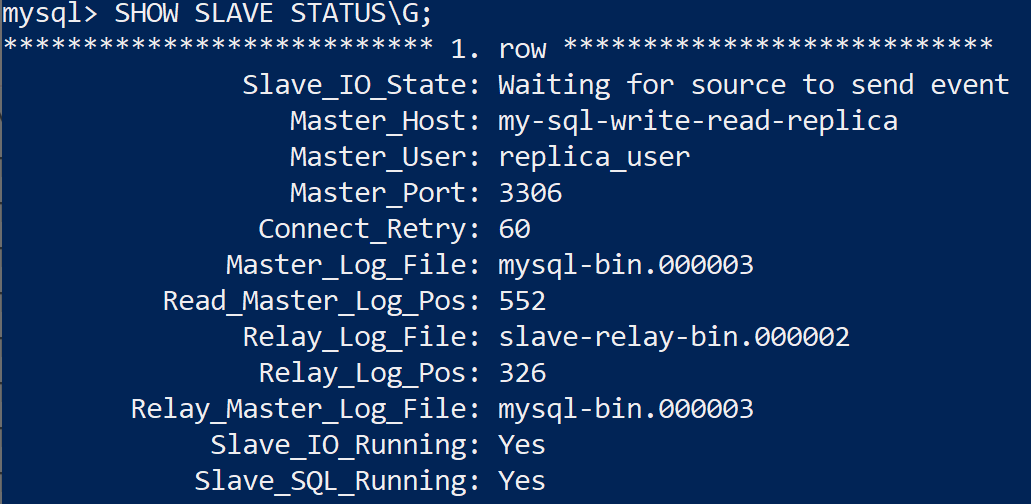
Note: ensure Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running is set to Yes
5. Configure Follower (Read Replica 2)
1. Connect to Read Replica 2
docker exec -it mysql-read-replica-2 mysql -u root -p2. Execute SQL
CHANGE MASTER TO
MASTER_HOST='my-sql-write-read-replica',
MASTER_USER='replica_user',
MASTER_PASSWORD='Replica1234!',
MASTER_SSL=1,
MASTER_SSL_CA='/etc/mysql/certs/ca-cert.pem',
MASTER_SSL_CERT='/etc/mysql/certs/client-cert.pem',
MASTER_SSL_KEY='/etc/mysql/certs/client-key.pem',
MASTER_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin.000003',
MASTER_LOG_POS= 552; 3. Start the Replica Node and Check Status
START SLAVE;
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G;Note: ensure Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running is set to Yes
6. Configure Follower (Read Replica 3)
1. Connect to Read Replica 3
docker exec -it mysql-read-replica-3 mysql -u root -p2. Execute SQL
CHANGE MASTER TO
MASTER_HOST='my-sql-write-read-replica',
MASTER_USER='replica_user',
MASTER_PASSWORD='Replica1234!',
MASTER_SSL=1,
MASTER_SSL_CA='/etc/mysql/certs/ca-cert.pem',
MASTER_SSL_CERT='/etc/mysql/certs/client-cert.pem',
MASTER_SSL_KEY='/etc/mysql/certs/client-key.pem',
MASTER_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin.000003',
MASTER_LOG_POS= 552; 3. Start the Replica Node and Check Status
START SLAVE;
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G;Note: ensure Slave_IO_Running and Slave_SQL_Running is set to Yes
7. Test the Replication
1. Execute SQL on the Leader Node
USE ecommerce_db;
CREATE TABLE Customers (
CustomerID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
FirstName VARCHAR(50),
LastName VARCHAR(50),
Email VARCHAR(100)
);
INSERT INTO Customers (FirstName, LastName, Email)
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com');2. Execute SQL on Read Replica 1
USE ecommerce_db;
SELECT * FROM Customers;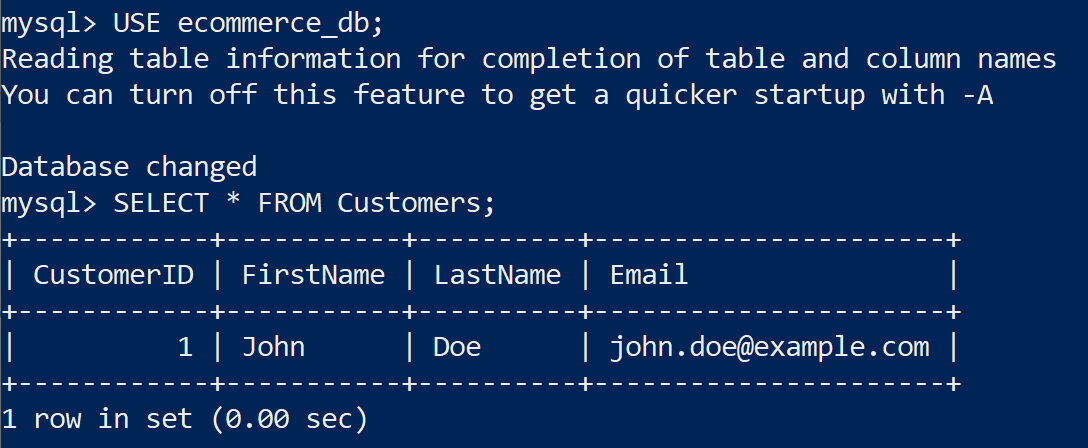
3. Execute SQL on Read Replica 2
USE ecommerce_db;
SELECT * FROM Customers;
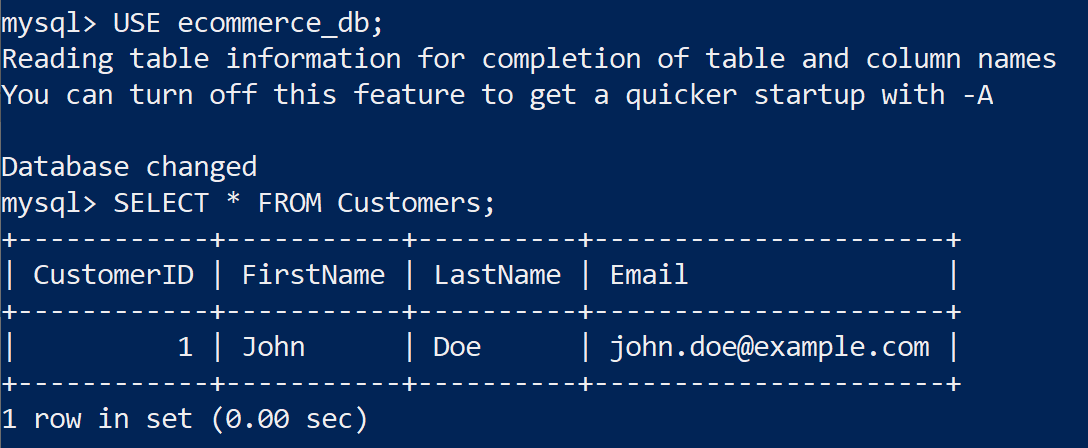
4. Execute SQL on Read Replica 3
USE ecommerce_db;
SELECT * FROM Customers;
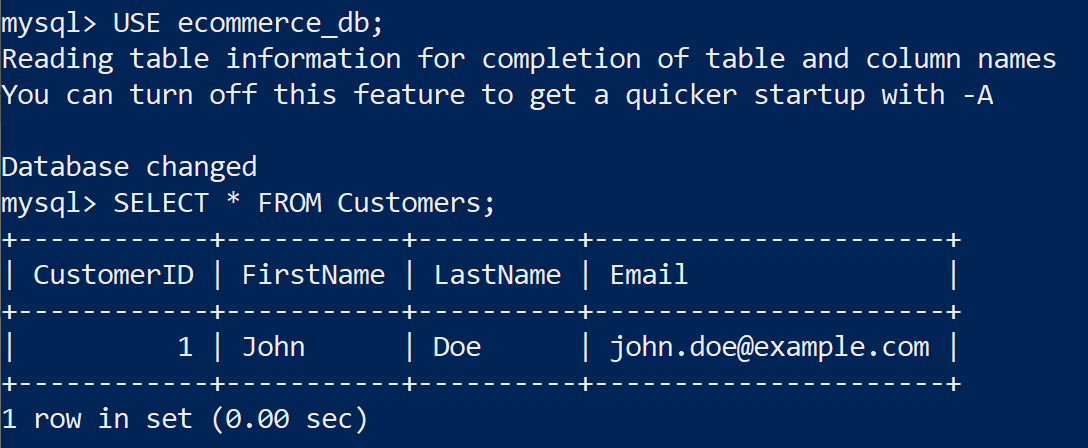
We can see consistent results on all read replicas.
8. Let's try inserting data into Read Replica 1
1. Access Read Replica 1
docker exec -it mysql-read-replica-1 mysql -u replica_user -p2. Execute SQL
USE ecommerce_db;
INSERT INTO Customers (FirstName, LastName, Email)
VALUES ('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com');Inserting into the database from the read replica is denied:

Pros and Cons of Single Leader Replication
Single Leader Replication allows one leader to co-ordinate all writes. This ensures data consistency for follower nodes. With one leader handling all write operations, there is no need for conflict resolution strategies. However, since there is only one leader co-ordinating all write operations, the leader itself becomes a single point of failure. Write scalability is also limited.